Troubles Art
Explore a range of responses to the Troubles by artists from Northern Ireland and beyond. (Part of the Art & The Troubles Series)
Rita Donagh
Born Wednesbury, Staffordshire, 1939

BELUM.U2509 © Ms Rita Donagh
Rita Donagh studied Fine Art at the University of Durham between 1956 and 1962. She taught at the University of Newcastle upon Tyne where she met fellow artist Richard Hamilton whom she later married.
In the 1960s her work was conceptual but by the 1970s the Troubles was a major focus in many of her artworks. Due to her Irish ancestry and the political situation in Northern Ireland. This painting is from a series entitled Disturbance. It was a reaction to a bombing in Talbot Street, Dublin, on 17 May 1974. The no-warning bomb was one of three planted by the loyalist Ulster Volunteer Force. All exploded within minutes of each other resulting in 26 people being killed and 140 injured.
Donagh reacted to a press image which showed the body of a young woman lying in the street covered with newspapers. She references Northern Ireland with an outline map. Belfast is marked in red as if bleeding from the violence of the conflict.
Graham Gingles
Born Larne, Co. Antrim, 1943

Graham Gingles studied at both the Belfast and Hornsey Colleges of Art. He began his artistic career as a painter but is best known for his distinctive sculpture in the form of meticulously constructed boxes.
Gingles has commented that at the beginning of the Troubles he found it necessary ‘to find an imagery that was not reportage, that was not graphic, that was not horrible in itself, but which made allusions without describing’. He explains his boxes as being about ‘public themes’ and politics but they are also autobiographical and reflect personal memories.
F.E. McWilliam
Born Banbridge, 1909

BELUM.U2438 © The Estate of F.E. McWilliam
After attending the Belfast College of Art, Frederick Edward McWilliam left Northern Ireland in 1928 to continue his training at the Slade School of Art, London. He lived and worked for most of his life in London, teaching sculpture at the Slade until 1968.
McWilliam often worked in series. Woman in Bomb Blast 1974/1 is the last and largest sculpture from a series called Women of Belfast which, he explained, ‘was concerned with violence, with one particular aspect, bomb-blast – the woman as victim of man’s stupidity’. Although they can be read as a metaphor for women affected by violence, these sculptures were McWilliam’s response to the Provisional IRA bombing of the Abercorn Restaurant in the centre of Belfast on 4 March 1972. The bomb exploded in the restaurant which was packed with Saturday afternoon shoppers, killing two women and injuring some 70 other people.
Joseph McWilliams
Born Belfast, 1938

BELUM.U2015.8 © Courtesy of the artist
Joseph McWilliams attended the Belfast College of Art and went on to teach there until his retirement in 1989. Since 1986 he has run the Cavehill Gallery in North Belfast with his artist wife Catherine McWilliams.
McWilliams responded to the Troubles from the outset, reacting, as he said in 1989, 'simply and safely in paint'. He sometimes incorporated other materials and found objects to replicate what he termed the 'physicalness' of violence. The door in this piece is the actual firebomb-damaged door from the Alliance Avenue Resource Centre in North Belfast where McWilliams was involved in community education. The rainbow often appears in his work, possibly a connotation of light and optimism in the midst of the darkness of the Troubles.
Philip Napier
Born Belfast, 1965

Philip Napier studied at Manchester Polytechnic, Falmouth School of Art, Cornwall and the University of Ulster where he was awarded an MA in Fine Art in 1989. Known for his work in sculpture, installations and performance, he is currently Head of the Faculty of Fine Art at the National College of Art and Design in Dublin.
Ballad No. 1 is based on one of the most recognisable images from the Troubles, that of Provisional IRA hunger striker Bobby Sands who died in 1981. Napier re-creates the image using the buttons of the accordion, an instrument ‘shared’ by the two communities in Northern Ireland. Napier’s work explores issues of power and cultural identity, often incorporating movement and sound.
Victor Sloan
Born Dungannon, Co. Tyrone, 1945

(Arts Council of Northern Ireland Collection, gifted in 2011).
BELUM.2012.3.213 © Victor Sloan
Victor Sloan studied painting at Belfast and Leeds Colleges of Art. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Arts and the Royal Photographic Society. His work is highly distinctive, created through altering photographs and negatives by painting, marking and scoring.
Sloan usually produces works as a series. Made in the aftermath of the Anglo-Irish Agreement of 1985, the Drumming series reflects the tensions surrounding annual Orange Order marches. Sloan has commented that these images contain anger, frustration and violence: ‘It’s not only coming from me, but it could be coming from another community towards this community, or from this community that I photographed, to the other community’.
Rita Duffy
Born Belfast, 1969

Rita Duffy received her MA in Fine Art at the University of Ulster in 1986. Her work, in which she uses a range of media, is often autobiographical and addresses subjects relating to Irish identity, history and politics. She has also commented that ‘women’s issues and feminism seem obvious and important concerns for me as an artist’.
In Security Barrier, the dome of Belfast’s City Hall looms over a familiar sight during the Troubles. For a period of time, a series of security gates formed a ‘ring of steel’ around the city centre. People entering this zone were subjected to body searches and their belongings were checked. The work references themes of control, security and a siege mentality.
John Keane
Born Hertfordshire, 1954

BELUM.U5068 © John Keane
John Keane studied painting at the Camberwell School of Art in London. Conflict has been a consistent theme in his work, driven by an interest in ‘why human beings want to kill one another for political ends’. Keane has travelled across the world to record conflict in situations such as Angola and the Gulf War.
The Other Cheek? is from a similarly titled series of paintings made between 1989 and 1990. It relates to a phrase Keane said he had heard used by members of Sinn Féin, the Ulster Defence Association and the British Army: ‘What do you expect us to do – turn the other cheek?’ Many of the most recognisable elements of the Troubles are evident as is their imprint on both communities: suffering and loss, murals, flags and peace lines.
Ken Howard
Born London, 1932

BELUM.U5005 © Professor Ken Howard RA Estate
Ken Howard studied painting at the Hornsea College of Art and the Royal College of Art. On two occasions, in 1973 and 1978, he was commissioned by the Imperial War Museum to travel with and record the British Army in Northern Ireland.
Ulster Crucifixion, which Howard considers his finest work, is styled after an altarpiece. He has combined a representation of graffiti referencing history, politics, religion and an army, recognised by him as elements of the crucifixion of Christ, with a depiction, based on an earlier drawing, of a young boy playing on a lamp post. It was painted at a time when he was becoming concerned with the plight of children in Northern Ireland. Speaking in 2005, Howard recalled that he ‘felt like the children were losing their childhood because of what was going on’.
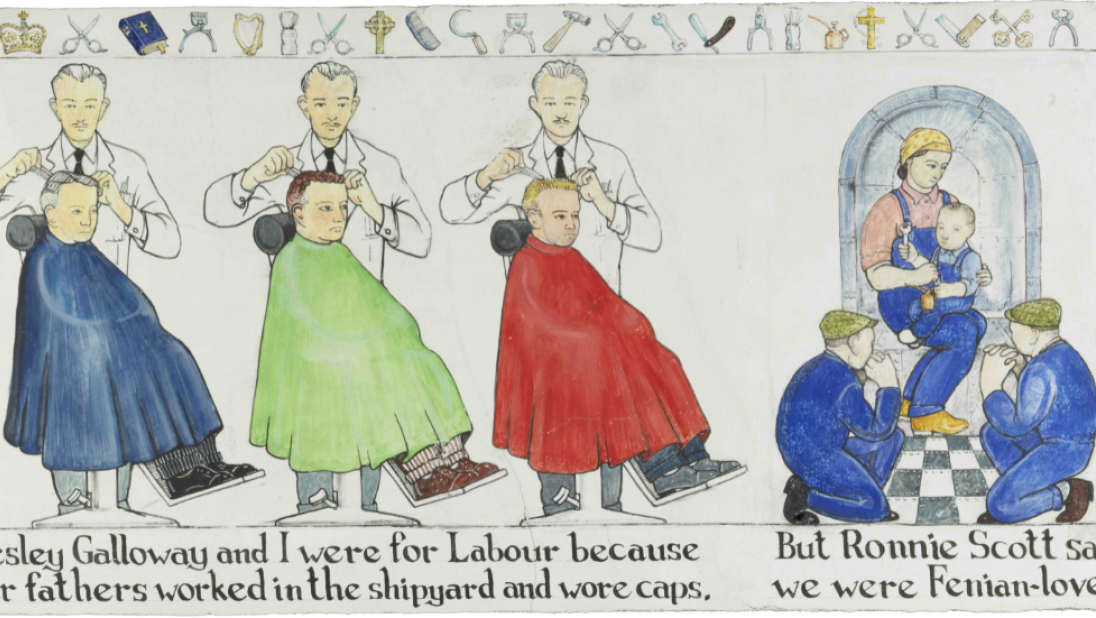
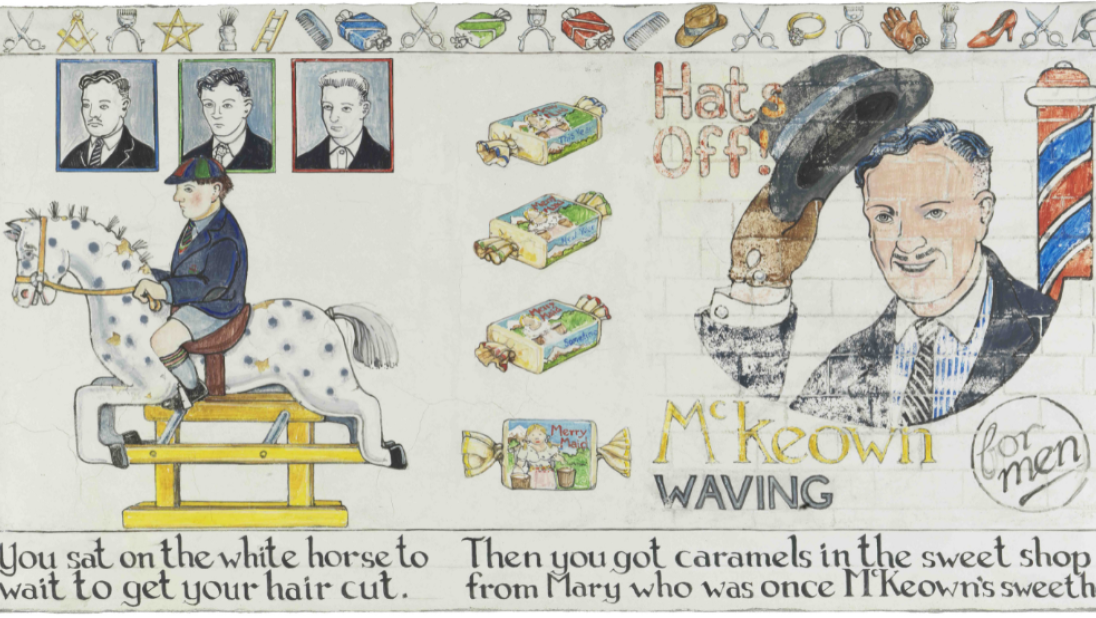
John Kindness
Born Belfast, 1951
Belfast Frescoes, 1994, John Kindness (born Belfast, 1951)
Series of 20 panels, lime fresco on roof slate
Each panel 30.5cm x 61cm
BELUM.U5038
John Kindness studied at the Belfast College of Art between 1970-1974. After completing his training, he worked as both a graphic designer and artist, focusing exclusively on art from 1986 onwards. He uses a wide variety of materials and is renowned for public sculptures, including the ‘Big Fish’ on Donegall Quay in Belfast.
Kindness was influenced by satirical cartoonists and has regarded humour as important in his work. Belfast Frescoes uses the vehicle of a comic strip to examine his childhood. By the end of the story his childhood perception of the divide and rule politics of Northern Ireland, which has influenced his work throughout his artistic career, has become evident. Kindness also uses how ‘a child can get things hilariously wrong, like the association with the white rocking horse in the barbers with King Billy’s steed’, to provide humour to the political situation.
The Ulster Museum has the largest collection of artistic responses to the Troubles however it cannot be seen as complete. Since the Art of the Troubles exhibition in 2014 the museum has continued to acquire artists’ work which was previously not represented in the collection. During this process, more artists and artworks continue to be uncovered and the collection continues to grow, alongside a complementary archive that relates to the artworks and the artists.
Explore more
History Galleries
Learn and explore local and global stories in our History Galleries.
Hannah Starkey
An exhibition in partnership with Belfast Photo Festival.
Colin Davidson, Silent Testimony
An exhibition of portrait paintings by Colin Davidson, reveals the stories of eighteen people who are connected by their individual experiences of loss through the Troubles.